Prof. Annika Kurzmann has been appointed ML4Q Professor for Experimental Solid-State Physics at the University of Cologne.
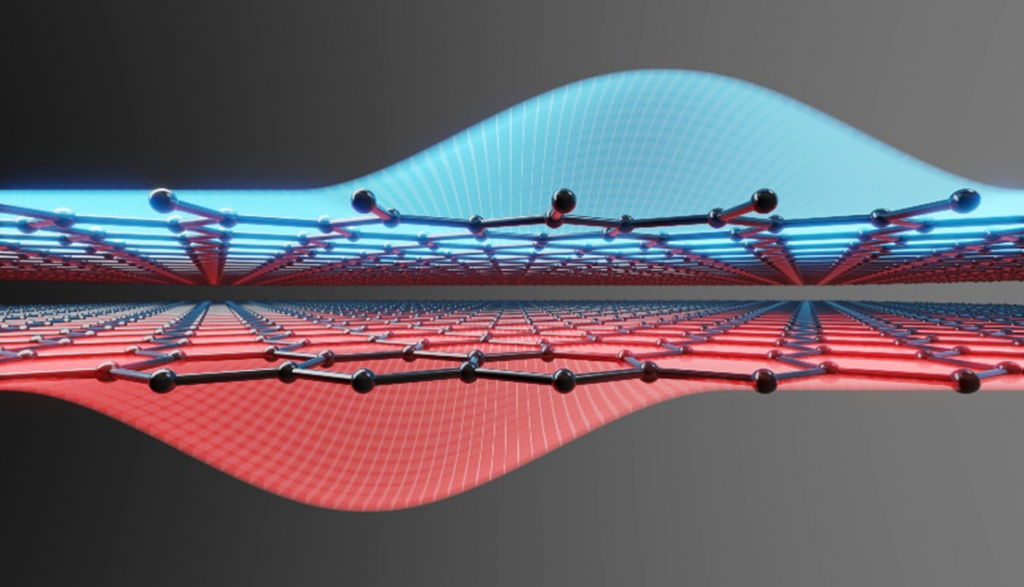
Continue reading “Congratulations to Prof. Annika Kurzmann”Interlayer transfer of valley polarization from excitons to free charge carriers in WSe2/MoSe2 heterobilayers
Scientists from RWTH Aachen, AMO GmbH, Forschungszentrum Julich and the University of Regensburg have shown that in twisted heterobilayers of WSe2 and MoSe2 there is a transfer of valley polarization from excitons in WSe2 to free carriers in MoSe2. This mechanism, which is strongly dependent on the twist angle, may allow the realization of opto-valleytronic devices where the valley polarization is optically excited but extracted and measured by electrical means. The results are reported in npj 2D Materials and Applications.

Congratulations to Prof. Alwin Daus
Alwin Daus has been appointed Junior Professor at the Department of Microsystems Engineering (IMTEK) at University of Freiburg.
Continue reading “Congratulations to Prof. Alwin Daus”Near perfect particle-hole symmetry in graphene quantum dots
Researchers at RWTH Aachen University and Forschungszentrum Jülich have uncovered important characteristics of double quantum dots in bilayer graphene, an increasingly promising material for possible applications in quantum technologies. The team has demonstrated near-perfect particle-hole symmetry in graphene quantum dots, which could lead to more efficient quantum information processing. The study has been published in Nature.
A scalable pathway for the mechanical transfer of graphene grown by CVD
Nowadays it is possible to grow high-quality graphene on large scale using chemical vapor deposition (CVD). What remains a major bottleneck for the industrialization of the material is the transfer of graphene from the growth substrate to a target one. A team of researchers from the University of Cambridge and RWTH Aachen University has now developed a methodology for optimizing simultaneously the growth and the transfer process, showing that it is possible to dry-transfer graphene with high-yield, if the crystallographic orientation of the growth surface is chosen appropriately.

(© Stampfer Lab, RWTH Aachen University)
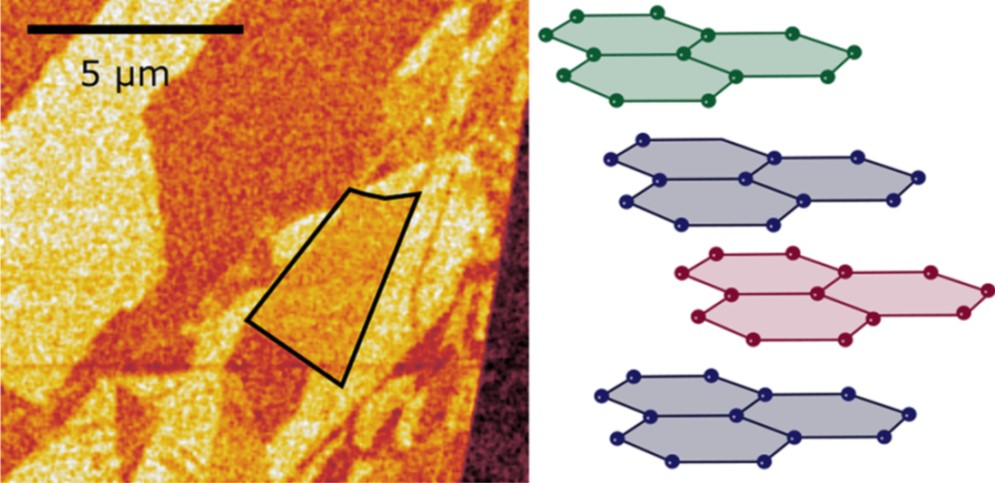
First experimental observation of an elusive stacking order in tetralayer graphene
Using advanced spectroscopic techniques, researchers from RWTH Aachen University have been able to observe for the first-time domains of tetralayer graphene with ABCB stacking. The results have been reported in ACS Nano.
Enhancing Biosensor Response with Graphene “Lighting-Rods” – A talk by Prof. Steven Koester
October 11, 2022, Prof. Steven Koester, from the University of Minnesota, has presented some of the latest results of his group on graphene-based bio-sensors during the 31th Aachen Graphene Center Seminar.
Continue reading “Enhancing Biosensor Response with Graphene “Lighting-Rods” – A talk by Prof. Steven Koester”How to report and benchmark emerging field-effect transistors
One of the challenges encountered by research on novel electronic devices is to compare devices based on different materials in a consistent way. RWTH Professor Max Lemme and colleagues from USA, China, and Belgium have now proposed a set of clear guidelines for benchmarking key parameters and performance metrics of emergent field-effect transistors. The guidelines have been published as a Perspective Article in Nature Electronics.
Continue reading “How to report and benchmark emerging field-effect transistors”Welcome to Mr. Saketh Ravuri and Ms. Priyanka Mondal
Mr. Saketh Ravuri and Ms. Priyanka Mondal have joined the “2D Materials and Quantum Devices Group” lead by Prof. Christoph Stampfer at RWTH Aachen University for a seven-month research staying supported by DAAD KOSPIE scholarships.
Continue reading “Welcome to Mr. Saketh Ravuri and Ms. Priyanka Mondal”New perspectives on Layer Transfer and Artificial Crystalline Heterostructures at IKZ – A talk by Dr. Jens Martin
Dr. Jens Martin, from the Leibniz-Insitut für Kristallforschung (IKZ) in Berlin, has been the speaker of the 30th Aachen Graphene Center Seminar. Dr. Martin is the head of the section Semiconductor Nanostructures at IKZ, and one of the coordinators of the IKZ-IRIS Joint Lab “Layer Transfer for 2D-Heterostructures“. In his talk, presented the recent advances of his group on the growth, release and transfer of thin epitaxial perovskite films, as well in on the in-situ growth of 2D-vdW multilayers and heterostructures.
Continue reading “New perspectives on Layer Transfer and Artificial Crystalline Heterostructures at IKZ – A talk by Dr. Jens Martin”